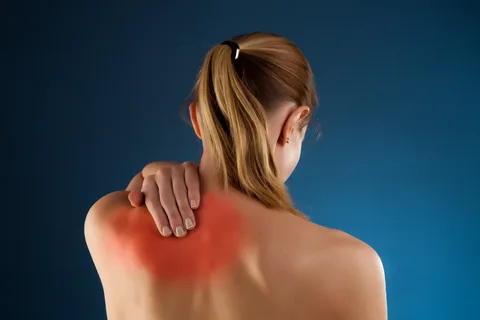
Usually, your cervical spine region has six discs, each located between the vertebrae that stack up to make the spine. These discs absorb shock and prevent the vertebrae from rubbing against each other as the neck moves. Discs are mostly made of water, but they naturally lose hydration as you advance in age. Over time, discs also begin to break down due to natural wear and tear; a condition called cervical disc disease. Almost everyone will develop cervical disc disease, Roswell, at some time due to age. The typical symptom of cervical disc disease is neck pain, but people may also experience other symptoms. But first, how does disc degeneration happen? Here is how.
The course of cervical degenerative disc disease
Cervical degenerative disc disease is technically not a disease but a descriptive term of the degenerative process that discs in the cervical spine go through. Most adults with degenerative disc disease have no symptoms, even though a high percentage show degenerative changes on imaging tests on the spine. About half of people start showing signs of disc degeneration on the spine by their early 20s. Most people under 50 have disc degeneration, while more than 90% of people over 50 have it.
What are the symptoms of cervical disc disease?
Most people diagnosed with disc degeneration experience no symptoms. However, sometimes cervical disc degeneration can cause neck pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in your shoulders and arms. When these symptoms become chronic, they are primarily associated with disc degeneration, including spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, and herniated discs. Whether symptoms are temporary or permanent depends on the cause of the degeneration. For example, pain from herniated discs often goes away without treatment, but that osteoarthritis requires long-term treatment.
Risk factors for cervical disc disease
Although anyone who lives long enough will develop disc degeneration, some people are more likely to develop the disease sooner and become symptomatic. Below are factors that elevate your risk of cervical disc disease.
- Obesity
Weight is associated with a risk of developing degenerative disc disease. When you are overweight, your body exerts extra pressure on the spinal discs, causing or accelerating degeneration. For example, excess upper body weight puts you at risk of lumbar disc disease. For this reason, specialists recommend losing weight and maintaining your ideal weight to lower your risk of disc degeneration and other problems like hypertension, heart disease, and sleep apnea.
- Genetics
Genetics significantly determine when cervical degenerative disc disease develops and whether it becomes painful.
- Smoking
Smoking is a bad habit that also constricts blood vessels in your body. As a result, your spinal discs have limited oxygen and nutrient supply. Eventually, the discs become dehydrated more quickly. Additionally, this inhibits natural repair in case of a tear or injury. Quitting smoking reduces your risk of disc degeneration and severe conditions like lung and colon cancers.
Although disc degeneration is often a result of age, it can also be influenced by lifestyle factors.
For further questions about cervical disc disease, consult your provider at Apex Spine and Neurosurgery.