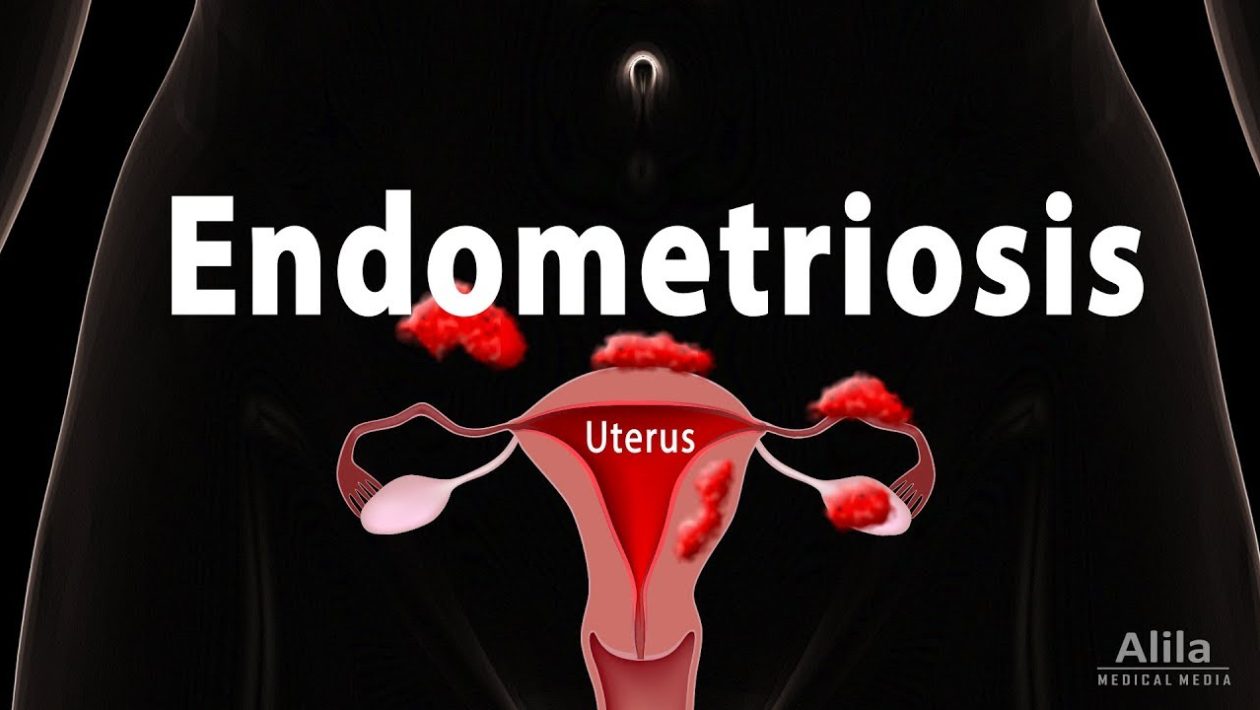
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue that typically develops inside the uterus grows outside the uterus, most frequently in the pelvic region. Endometriosis Jackson Heights symptoms differ from individual to individual. While some endometriosis patients experience excruciating pain and a deteriorating quality of life, others show no signs at all.
More than 11 percent of menstruating women in the United States between the ages of 15 and 44 have endometriosis. Although any woman who has started her periods can have this illness, there are risk factors that raise your likelihood of doing so.
Here are the risk factors for endometriosis:
- Family background
Your chance of getting endometriosis is 7 to 10 times higher than it is for those who don’t have a family history of this condition.
You are more likely to have endometriosis if one of your family members, like your mother, grandmother, sister, or other close relatives, has it. Your likelihood of having endometriosis is also increased if you have distant relatives who have it, such as cousins.
- Menstrual characteristics
Your risk of having endometriosis increases with your exposure to menstruation. Your risk is increased by factors that enhance your menstrual exposure, such as:
- Having short menstrual cycles, mostly less than 27 days
- Beginning your menstruation before becoming 12 years old
- Enduring heavy periods that last for more than seven days
The risk is lower while you are pregnant since you have fewer periods. Your symptoms may lessen during pregnancy if you have endometriosis and can get pregnant. After your kid is delivered, it’s normal for your symptoms to reappear.
- Age
Because endometriosis affects uterine lining cells, it can affect any girl or woman old enough to start menstruating. Despite this, women in their 20s and 30s are the majority of those who are diagnosed with endometriosis. According to experts, this is the age at which women begin attempting to conceive, and for some people, infertility is the primary sign of endometriosis. Women who do not have extreme menstrual pain might wait until they are trying to get pregnant to see their physician for a checkup.
- Abdominal surgery
Endometrial tissue can occasionally be misplaced after abdominal surgery, such as a hysterectomy or cesarean section (often known as a C-section).
Endometriosis may develop if your immune system does not eliminate this misplaced tissue. When addressing your endometriosis symptoms with your doctor, go through your surgical past.
- Uterine abnormalities
Uterine abnormalities increase the risk since they facilitate retrograde menstruation. These include disorders that affect the uterus’s position or block the menstrual flow. Some instances are:
- Uterine fibroids
- Uterine polyps
- Retrograde uterus (also referred to as a tilted uterus)- Uterus that bends backward rather than forward
- Congenital uterine abnormalities, such as cryptomenorrhea (in which menstruation occurs but cannot be seen due to a congenital obstruction)
- Immune system conditions
Immune system issues raise the chance of endometriosis. Your immune system’s capacity will affect its ability to detect displaced endometrial tissue. Endometrial tissue that is dispersed is allowed to implant in the incorrect locations. This can cause problems like inflammation, lesions, and scarring.
Understanding the endometriosis risk factors might help you take control of your health. This information can assist your doctor make a more precise diagnosis and give you practical risk-reduction suggestions.
Call Raveco Medical to book your appointment for endometriosis treatment.